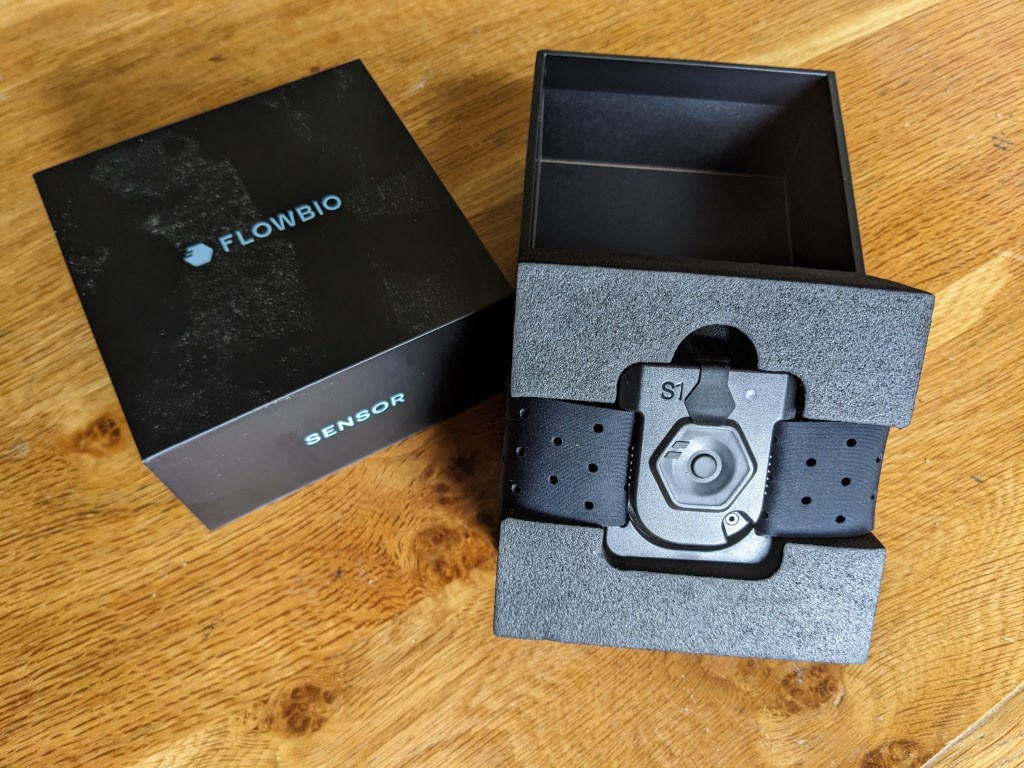
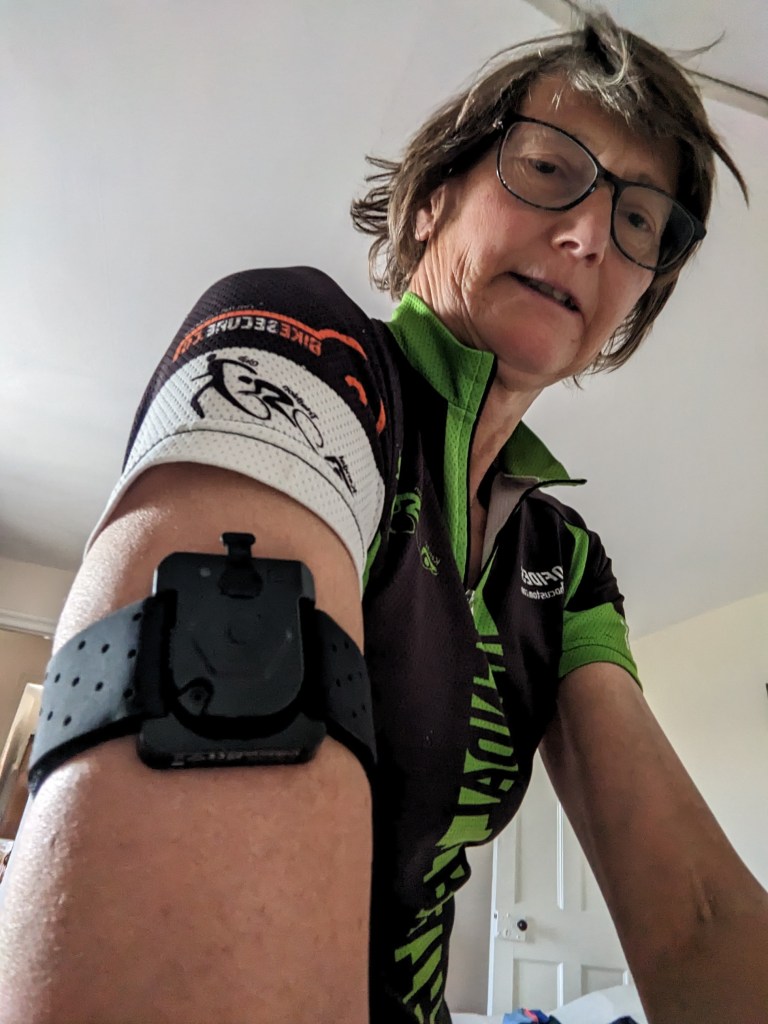
This is a great little gadget which I have found useful and easy to use. I have trialled it for a couple of months, with a bit of a gap when my watch died. I have tried to use it in different conditions and situations. It should arrive with you in a neat box containing the sensor, arm band for attaching, charging cable, two bottles for cleaning and two tiny plugs for the charging point to stop sweat getting into it.

Charge it, then protect the charging point with one of the tiny silicon covers provided. This prevents sweat entering the charging point. Download the app onto your phone. Sign in and follow the instructions. There is an app for both apple and android. I am working off android and I haven’t had any issues so it must be fairly simple. It asks you which of the main sports hydration brands you use, and it then uses this information to make it easier to enter what hydration you have taken in a session. Then you are ready to go.
Your first session the recommendation is to work out in temperatures above 20 degrees and to hold a HR of at least 130 for a minimum of one hour. I interpreted this as work just into zone 3 (garmin) and I was probably the lower side of this in our conservatory and it seemed to work ok. After that sessions need to be longer than 30 mins to generate sufficient data. It will only work for cycling and running, no other sessions currently. It can be used when racing triathlon, it can be worn safely under a wetsuit but will not record on the swim, only on the bike and run.
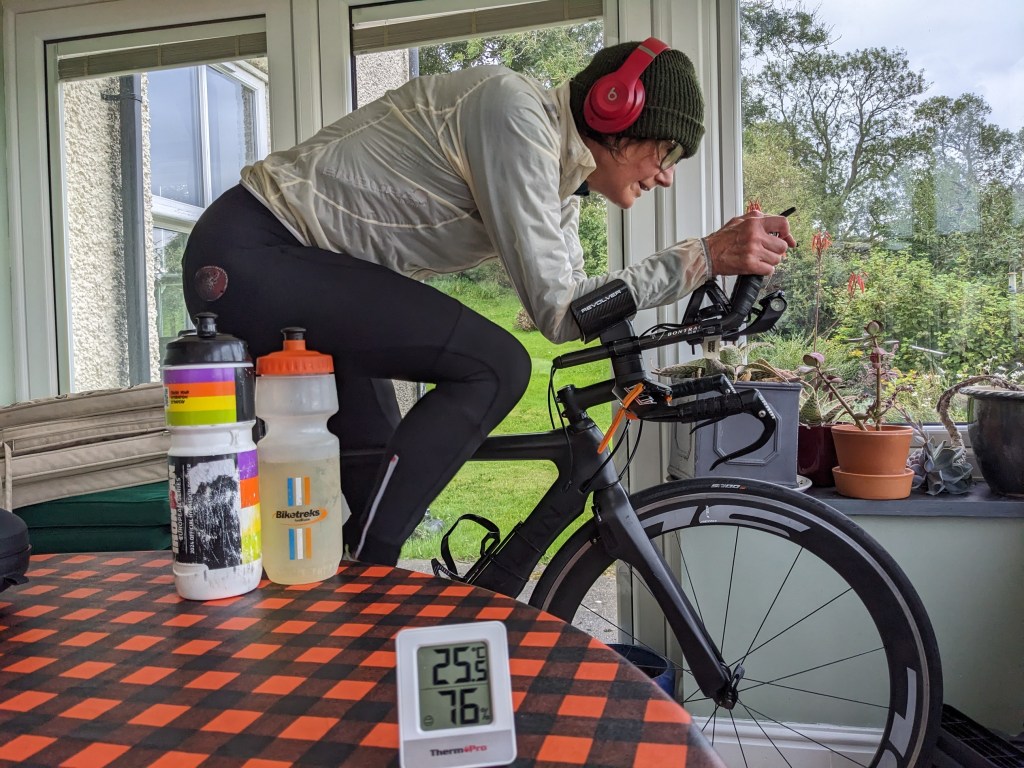

Before a session put the arm band around your arm and tighten it. Then turn the sensor on by pressing the button in the middle for two seconds. Lights will flash green. Also turn on your tracking device – garmin or whatever.
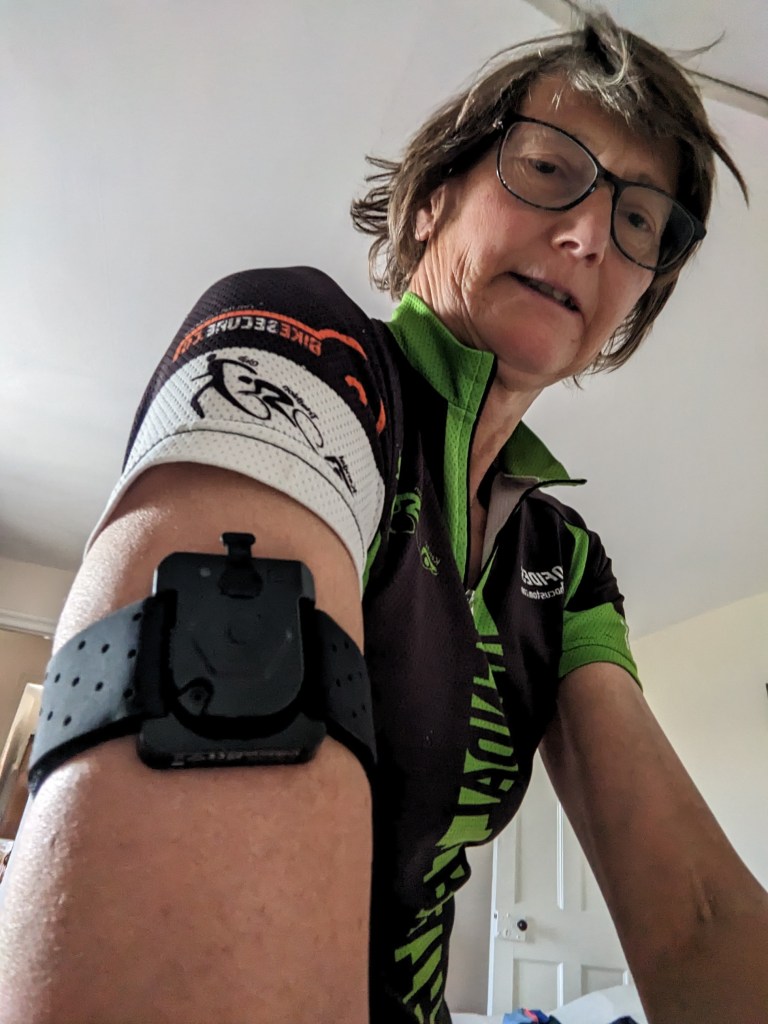
Complete your session. Turn the device off by pressing the button in the middle for two seconds. The light will go clear then turn off. Finish your session on your tracking device and encourage the sensor to synch with the app. I find this easiest by going into the App and ‘settings’ and pressing ‘Sensor connection’. When connected the light on the sensor will turn blue. Then, after a while, your app will display information concerning your use of sodium and loss of fluid during your session. You have the option to upload the quantity of fluid and sodium you have consumed to the app if you wish. The app will then work out the recommendation for refuelling sodium and fluid to replace losses from the session. You can obviously work them out yourself if you choose.
It also enables you to put in data for your next session – distance, sport, effort etc, and it will then work out your fluid and sodium needs. Clever bit of kit.
| Date | Session | Length Hr Min = m | Temp C | Sweat loss (Litres) | Sweat loss L/hr | Sodium Loss mg | Sodium Conc Mg/L | Comment |
| 27/8 | Cycle medium | 1 hr | 0.42 | 0.47 | 493 | 1160 | Heat training indoors | |
| 28/8 | Cycle easy | 1 hr | 13.3 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 471 | 2024 | |
| 28/8 | Run easy | 30 m | 14.2 | 0.21 | 0.40 | 192 | 907 | |
| 29/8 | Cycle medium | 1:18 | 0.37 | 0.30 | 513 | 1373 | OGE indoors | |
| 31/8 | Run easy | 1:16 | 18.4 | 0.70 | 0.60 | 752 | 1079 | |
| 31/8 | Run hard | No data | ||||||
| 2/9 | Cycle medium | 44m | 25.5 | 0.37 | 0.52 | 439 | 1175 | Heat training & OGE indoors |
| 7/9 | Cycle hard | 1:32 | 16.9 | 0.84 | 0.57 | 1823 | 2175 | Racing triathlon |
| 7/9 | Run hard | 1:02 | 16.9 | 0.70 | 0.68 | 800 | 1139 | Racing triathlon |
| 14 Sept | Bike medium | 3:14 | 11 | 1.17 | 0.38 | 1597 | 1366 | Racing triathlon |
| 14 Sept | Run med | 2:10 | 14.5 | 1.26 | 0.58 | 1710 | 1360 | Racing triathalon |
| 19 Sept | Bike Med | 2:30 | 16.8 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 971 | 1297 | mtb |
| 21 Sept | Bike Easy | 1:30 | 12 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 355 | 1395 | |
| 23 Sept | Bike Easy | 1.24 | 10 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 281 | 1311 | |
| 24 Sept | Run Easy | 41min | 10 | 0.19 | 0.27 | 255 | 1343 | |
| 26 Sept | Walk Fell | 5:39 | 12.8 | 1.10 | 0.23 | 1786 | 1625 | Fell walking |
| 27 Sept | Walk Fell | 5:35 | 13.7 | 0.62 | 0.17 | 592 | 958 | Fell walking |
| 30 Sept | Bike Medium | 1:05 | 20 | 0.35 | 0.34 | 437 | 1240 | Heat training indoors |
| 20 October | Run hard | 51:02 | 13.1 | 0.44 | 0.51 | 629 | 1446 | Duathlon race |
| 20 October | Bike hard | 1:19:02 | 13.7 | 0.39 | 0.31 | 503 | 1299 | Duathlon race* |
*Watch didn’t record last run.
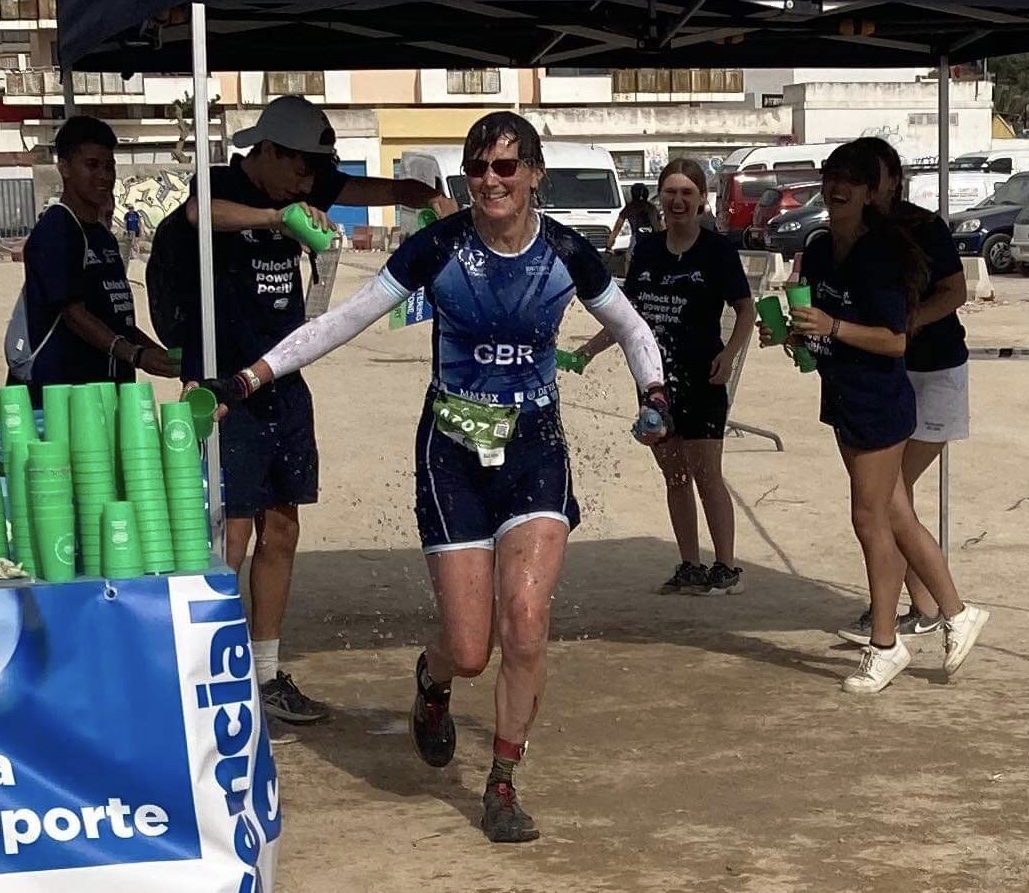
Racing Vitruvian middle distance, 14th September, with sensor on my arm.
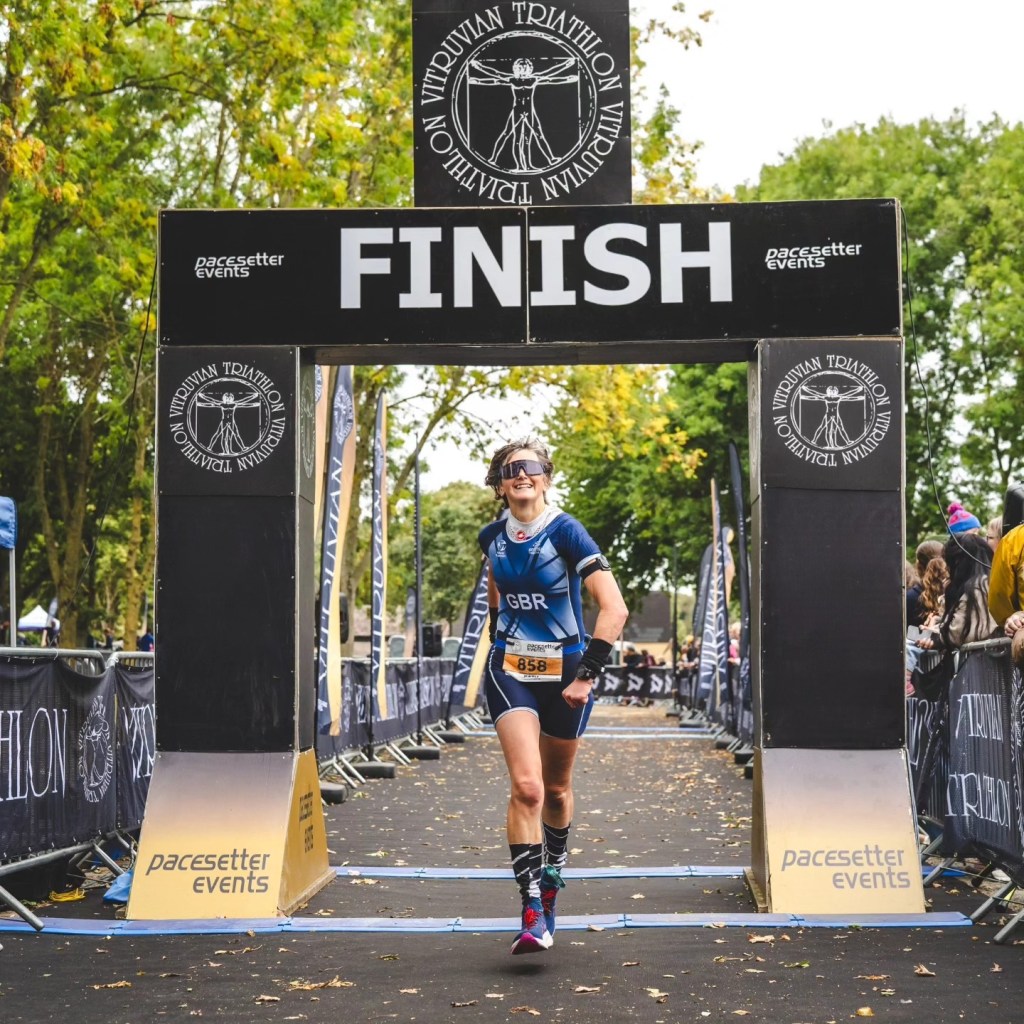

My sodium concentration is about 1300mg/L, give or take a bit. So most of the main brands of sports fuel need additional salt added. I should be at 650mg per 500ml.
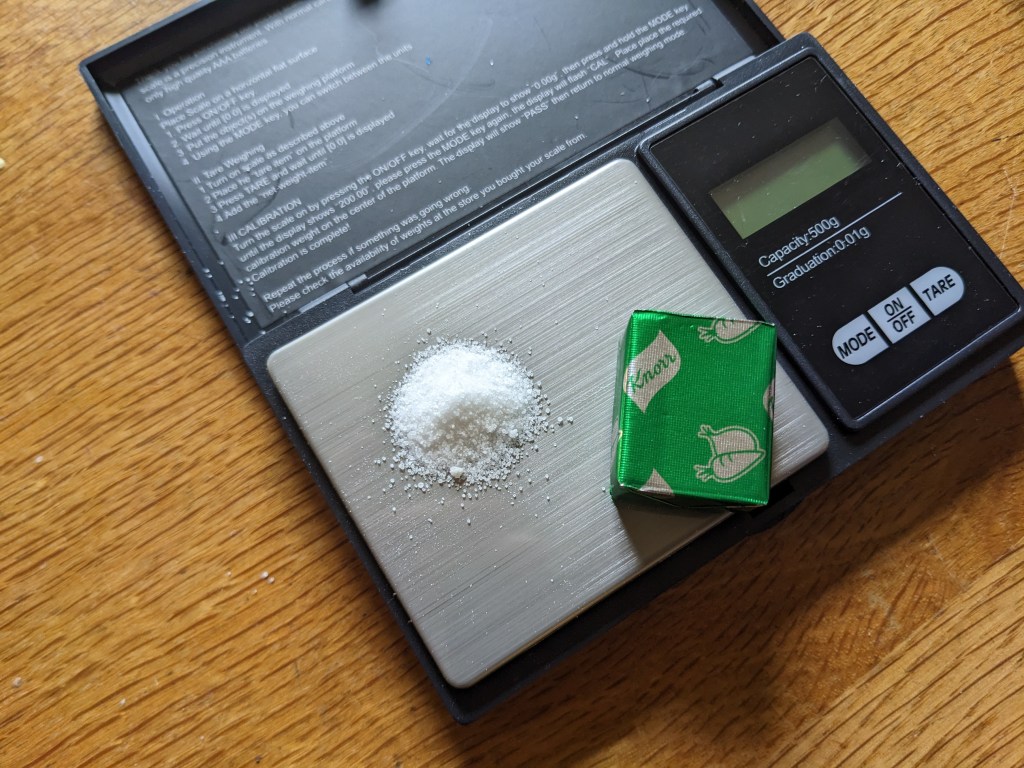
Some sports drinks have some sodium added, some don’t. The amount in most drinks is often insufficient to replace our losses. Additional salt tablets or sticks are options as is table salt. If you use salt in your own drinks you avoid the acid which is in most electrolyte tabs, so that is better for your teeth. Remember a gram of salt is 40% sodium and 60% chlorine. There are 387mgs of sodium in a gram of salt. Microscales enable you to weight these quantities accurately and are very cheap to buy. Adding salt to sports drinks eg SiS Beta fuel also helps dampen the sweet taste and can make them more tolerable. A gram of salt is shown on the microscales below with a stock cube for scale.

| Brand | Sodium mg Per 500ml |
| SiS electrolyte tab | 345 |
| Precision Hydration 1000 tab | 500 |
| Styrkr electrolyte tab | 500 |
| Beta fuel (SiS) | zero |
| Styrkr drink mix | 54 |
| SiS gel | 4 |
| Bulk hydration drink | 255 |
| Skratch drink | 400 |
The sensor doesn’t take account for your sodium intake in your diet, so consider that. There are also some thoughts around it’s accuracy – like any gadget it isn’t foolproof. According to their FAQs the accuracy rate for sodium loss is 90% in lab conditions and 83% in the field. Fluid is 73% accurate, with as little as 250ml difference to in-field gold standards. Not perfect but better than nothing and we often forget that data is frequently only an approximation eg your garmin sleep data.
But at least it should show you that a policy of ‘nil by mouth’ training isn’t going to give you the best results for your efforts. Hopefully it will help on my constant quest to persuade people to eat and drink sufficient fuel for training.